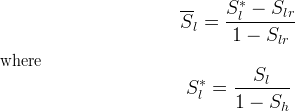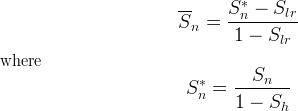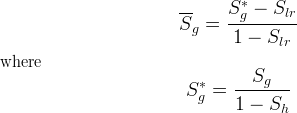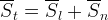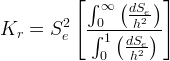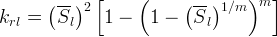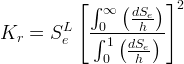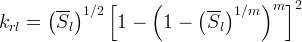Aqueous Relative Permeability Options (HYDT-KE)
Effective Saturations
Mobile saturations are normalized by the hydrate saturation and scaled by the residual aqueous liquid saturation to determine effective saturations for use with common relative permeability models.
Relative Permeability Models
Constant: the relative permeability is constant regardless of saturation.
Burdine:
Mualem:
Free Corey:
Modified Mualem: the pore scale parameter (aka tortuosity-connectivity coefficient) can be any value
STOMP User Guide Home
- Simulation Title Card
- Solution Control Card
- Grid Card
- Inactive Nodes Card
- Rock/Soil Zonation Card
- Mechanical Properties Card
- Hydraulic Properties Card
- Saturation Function Card
- Aqueous Phase Relative Permeability Card
- Gas Phase Relative Permeability Card
- NAPL Phase Relative Permeability Card
- Thermal Properties Card
- Salt Transport Card
- Initial Conditions Card
- Boundary Conditions Card
- Source Card
- Output Control Card
- Surface Flux Card