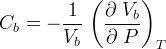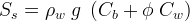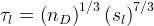Mechanical Properties Card Options (CO2E)
Compressibility Options
Geologic media in STOMP-W is considered to be slightly compressible. Compressibility is considered to be an intrinsic property of a rock/soil type. Compressibility can be specified via three options:
Sub-Options
Either or both of the following options can be used with any of the Compressibility Options.
Tortuosity Functions
Tortuosity functions are required for simulations that involve solute transport or diffusion of components through phases (e.g., water vapor diffusing through the gas phase or dissolved oil diffusing through the aqueous phase). Tortuosities can be computed either as:
References
Marshall, T. J. (1959), The diffusion of gases through porous media. J. Soil Sci., 10, 79–82, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2389.1959.tb00667.x.
Millington, R. J. and J. P. Quirk. 1959. Permeability of porous media. Nature 183:387-388.
STOMP User Guide Home
- Simulation Title Card
- Solution Control Card
- Grid Card
- Internal Boundary Surfaces
- Inactive Nodes Card
- Rock/Soil Zonation Card
- Mechanical Properties Card
- Hydraulic Properties Card
- Saturation Function Card
- Aqueous Phase Relative Permeability Card
- Gas Phase Relative Permeability Card
- Thermal Properties Card
- Salt Transport Card
- Initial Conditions Card
- Boundary ConditionsCard
- Coupled Well Card
- Source Card
- Output Control Card
- Surface Flux Card