STOMP User Guide
STOMP User Guide
Mechanical Properties Card Options
The following material properties of the porous medium are specified in the Mechanical Properties Card. Each property must be specified for each rock type defined in the Rock/Soil Zonation Card. The options available for each property are described under the correponding tab.
Particle Density
Particle Density represents the rock grain density. This value will default to 2650 kg/m3 by using a null entry for both the particle density and its associated units. This parameter must be specified for each rock/soil type. If the Rock/Soil name is "IJK Indexing," "JKI Indexing," or "KIJ Indexing," then the value specified will be applied to all nodes in the domain. Alternately, any parameter value can be replaced with an external file.
Porosity
Total porosity and diffusive porosity are specified in this card. Total porosity refers to total connected and unconnected pore volumes and diffusive porosity refers to only the connected pore volume. It is common to use the same value for both porosities. This parameter must be specified for each rock/soil type. If the Rock/Soil name is "IJK Indexing," "JKI Indexing," or "KIJ Indexing," then the value specified will be applied to all nodes in the domain. Alternately, any parameter value can be replaced with an external file.
If the key words 'dp,' 'dual porosity,' or 'fractured' appear in the rock/soil name specified inthe Rock/Soil Zonation Card, this indicates a dual porosity medium and the reading of both matrix and fracture properties (e.g., Fracture and Matrix Total Porosity) is triggered.
Compressibility
Geologic media in STOMP are considered to be slightly compressible. Compressibility is considered to be an intrinsic property of a rock/soil type and can be specified as one of the following options:
Bulk Compressibility
Bulk compressibility is the change in the bulk rock volume with respect to change in pressure at constant temperature:
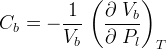
Bulk and pore compressibility can be related as::
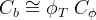
| Symbols | |
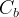 |
bulk compressibility, 1/Pa |
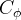 |
pore compressibility, 1/Pa |
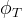 |
total porosity |
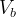 |
bulk volume, m3 |
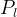 |
aqueous liquid pressure, Pa |
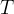 |
temperature, K |
Pore Compressibility
Pore compressibility is the change in pore volume with respect to change in pressure at constant temperature:
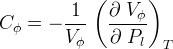
Bulk and pore compressibility can be related as::
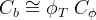
| Symbols | |
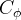 |
pore compressibility, 1/Pa |
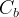 |
bulk compressibility, 1/Pa |
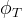 |
total porosity |
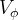 |
pore volume, m3 |
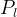 |
aqueous liquid pressure, Pa |
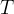 |
temperature, K |
Specific Storage
Specific storage is the amount of water that a portion of an aquifer releases from storage, per unit mass or volume of aquifer, per unit change in hydraulic head, while remaining fully saturated. Specific storage can be expressed in terms of water density, porosity, water compressibility, and bulk rock compressibility as:
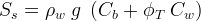
and
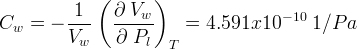
| Symbols | |
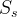 |
specific storage, 1/m |
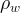 |
density of water, kg/m3 |
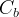 |
bulk compressibility, 1/Pa |
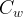 |
water compressibility, 1/Pa |
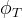 |
total porosity |
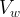 |
volume of water, m3 |
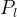 |
aqueous liquid pressure, Pa |
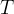 |
temperature, K |
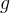 |
acceleration of gravity, m/s2 |
Specific storage is converted to bulk compressibility via the specified diffusive porosity and a standard compressibility of water. As with particle density, default values of specific storativity will be computed for null entries of both the specific storativity and its associated units. Default specific storativity is computed from the diffusive porosity and a default value of 1.x10–7 1/Pa for the compressibility.
This parameter must be specified for each rock/soil type. If the Rock/Soil name is "IJK Indexing," "JKI Indexing," or "KIJ Indexing," then the value specified will be applied to all nodes in the domain. Alternately, any parameter value can be replaced with an external file.
Tortuosity
Tortuosity functions are required for simulations that involve solute transport or diffusion of components through phases (e.g., water vapor diffusing through the gas phase or dissolved oil diffusing through the aqueous phase). Tortuosities can be computed either as:
Constant
When choosing the constant option, specific input values for the tortuosity factor may be specified.
Millington and Quirk
Tortuosity can be specified using functions of the phase saturation and diffusive porosity according to the formulation of Millington and Quirk (1959):
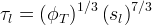
| Symbols | |
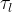 |
aqueous phase tortuosity |
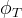 |
total porosity |
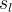 |
actual aqueous liquid saturation |
Marshall
Tortuosity can be specified using functions of the phase saturation and diffusive porosity according to the formulation of Marshall (1959)
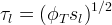
| Symbols | |
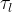 |
aqueous phase tortuosity |
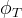 |
total porosity |
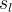 |
actual aqueous liquid saturation |
Marshall, TJ. 1959. The diffusion of gases through porous media. J. Soil Sci., 10, 79–82.
Millington, RJ. and JP Quirk. 1959. Permeability of porous media. Nature 183:387-388.