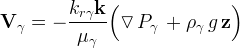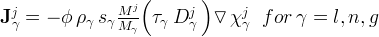Kinetic Component Mass Conservation Equations
The kinetic component mass conservation equations for hydrate formers (CH4, CO2, N2) in STOMP-HYDT-KE are shown. These equations equate the time rate of change of hydrate former mass within a control volume with the flux of hydrate former mass crossing the control volume surface. The conservation equations for hydrate formers include kinetic exchange between the mobile (m) and hydrate (h) phases and gross transport between the mobile and hydrate phases through kinetic hydrate formation and dissociation.
Mobile Component Mass Conservation Equations
Mobile CH4, CO2, and N2 are assumed to exist in the aqueous (l), nonaqueous liquid (n), and gas (g) phases under equilibrium conditions.
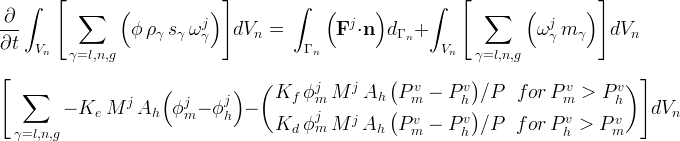
for each hydrate former component (j = CH4, CO2, N2).
Mobile Component Mass Flux
The flux of each mobile hydrate former is a combination of advective and diffusive components:
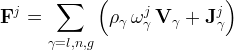
Hydrate Mass Conservation Equation
The conservation equation for hydrate mass includes kinetic exchange of hydrate formers between the mobile (m) and hydrate (h) and gross transport between the mobile and hydrate phase through kinetic hydrate formation:
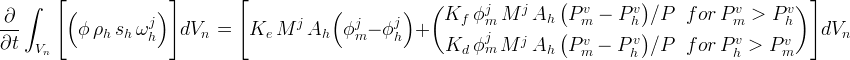
Symbols(In order of appearance) |
|
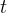 |
time, s |
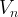 |
volume of element n, m3 |
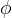 |
diffusive porosity |
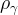 |
density of phase γ, kg/m3 |
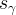 |
saturation of phase γ |
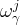 |
mass fraction of component j in phase γ |
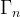 |
surface of element n, m2 |
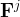 |
advective flux of component j, kg/m2s |
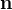 |
unit surface normal vector |
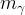 |
specific mass source of phase γ, kg/m3 s |
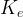 |
molar guest molecule exchange rate constant, kmol/ m2 s |
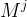 |
molecular weight of component j, kg/kmol |
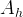 |
specific hydrate surface area, m2/m3 |
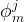 |
mole fraction of hydrate former j in mobile phases |
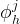 |
mole fraction of hydrate former j in solid hydrate phase |
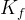 |
molar hydrate formation rate constant kmol/m2 s |
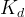 |
molar hydrate dissociation rate constant kmol/m2 s |
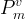 |
total vapor pressure of hydrate formers in mobile phase, Pa |
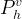 |
equilibrium hydrate vapor pressure, Pa |
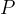 |
total pressure, Pa |
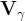 |
Darcy velocity vector of phase γ, m/s |
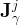 |
diffusive-dispersive flux of component j for the phase γ, kg/m2 s |
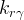 |
relative permeability of phase γ |
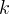 |
intrinsic permeability, m2 |
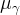 |
kinematic viscosity of phase γ, Pa s |
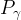 |
pressure of phase γ, Pa |
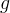 |
acceleration of gravity, m/s2 |
 |
unit gravitational direction vector |
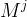 |
molecular weight of component j, kg/kg mol |
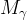 |
molecular weight of phase γ, kg/kg mol |
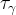 |
phase tortuosity for phase γ |
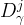 |
diffusion coefficient of component j for phase , m2/s |
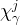 |
mole fraction of component j in phase γ |
| Subscripts | |
|---|---|
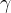 |
phase index |
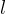 |
aqueous liquid phase |
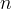 |
nonaqueous liquid phase |
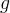 |
gaseous phase |
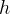 |
hydrate phase |
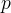 |
precipitated salt/inhibitor phase |
| Superscripts | |
|---|---|
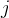 |
component index |