Source Card Options (W)
![]()
Aqueous Source Options
Aqueous Source Options
Aqueous Volumetric 
Source type where the aqueous fluid is injected/withdrawn into/from the node(s) at the specified aqueous volumetric rate during the indicated time period. The rate specified in the Source Card is for a single node. Therefore, if a source is applied over several nodes, the total aqueous volumetric rate of injection/withdrawal should be divided between these nodes.
Aqueous Volumetric Density 
Source type where the aqueous fluid is injected/withdrawn into/from the node(s) at the specified aqueous volumetric rate per unit volume (e.g., 1/m3) during the indicated time period. This option allows the user to have a uniform distribution of the aqueous volumetric rates over multiple source nodes with various dimensions.
Aqueous Mass 
Source type where the aqueous fluid is injected/withdrawn into/from the node(s) at the specified aqueous mass rate during the indicated time period. The rate specified in the Source Card is for a single node. Therefore, if a source is applied over several nodes, the total aqueous mass rate of injection/withdrawal should be divided between these nodes.
Aqueous Mass Density 
Source type where the aqueous fluid is injected/withdrawn into/from the node(s) at the specified aqueous mass rate per unit volume (e.g., 1 m3) during the indicated time period. This option allows the user to have uniform distribution of the aqueous mass rates over multiple source nodes with various dimensions. The rate specified in the Source Card is for a single node. Therefore, if a source is applied over several nodes, the total aqueous mass density rate of injection/withdrawal should be divided between these nodes.
![]() Solute Source Options
Solute Source Options
![]() Solute Source Options
Solute Source Options
Solute 
Source type where the solute is injected/withdrawn into/from the node(s) at the specified rate during the indicated time period. The rate specified in the Source Card is for a single node. Therefore, if a source is applied over several nodes, the total solute rate of injection/withdrawal should be divided between these nodes.
Solute Density 
Source type where the solute is injected/withdrawn into/from the node(s) at the specified solute rate per unit volume (e.g., 1 m3) during the indicated time period. This option allows the user to have uniform distribution of the solute rates over multiple source nodes with various dimensions.
Solute Inventory 
Source type that spreads the inventory uniformly over the domain based on the node volume. This results in a unique input source for each node included in the region of release. Two values, the domain solute inventory and the maximum solute concentration (e.g., 1/m3), are required. Solute inventory (mass) should be specified in the assumed units for solute (e.g., Ci, pCi, gm, kg, mol, kmol).
Solubility-Controlled Solute 
Source type that assumes that a solid controls the solution concentration in the aqueous phase of the constituents being released. The solute is injected into the node at a constant specified concentration (e.g., 1/m3) based on the solubility limits of a solid during the indicated time period. The total inventory mass is also specified so that the solute will only be injected until the total inventory source is depleted.
Solubility-Controlled Salt Cake 
Source type that assumes that a solid controls the solution concentration in the aqueous phase of the constituents being released. The Salt Cake release model is a variant of the Solubility-Controlled Solute release model so that the release rate is a constant rather than a variable dependent on the total mass at the source. When applied to residual tank wastes, the term “cake” applies to the sludge and hard heel residual in the tanks that compose the structural matrix. The salt cake source consists of a mathematical formulation containing a water flux, waste source thickness, and waste solid solubility term. Three values, the solubility (1/m3), the salt-cake waste volume (m3)), and the solute inventory (kg/m3) are required (Zhang et al. 2004)
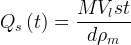
Symbols |
|
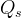 |
source release rate, 1/s |
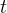 |
time, s |
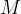 |
mass of waste, kg |
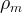 |
density of waste, kg/m3 |
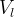 |
Darcy velocity of the aqueous phase, m/s |
 |
solute aqueous solubility, 1/m3 |
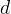 |
vertical depth of waste, m |
Solute Advection-Dominated
This source type is also known as the Mixing-Cell Cascade model. The advection-dominated model can be used to simulate releases from stabilized (grouted tank or tank ancillary) waste. For stabilized waste, the contaminants are released into the subsurface at a rate determined by both the rate of infiltrating water and the amount of dispersion occurring within the source which is assumed to contain a series of cascading, N equal-sized, well-stirred cells. Three values, the number of mixing cells, the source thickness (m), and the nodal solute inventory are required (Zhang et al. 2004)
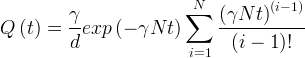
where
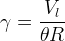
Symbols |
|
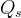 |
source release rate, 1/s |
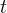 |
time, s |
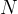 |
number of mixing cells |
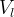 |
Darcy velocity of the aqueous phase, m/s |
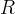 |
retardation factor |
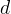 |
vertical depth of waste, m |
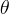 |
volumetric water content |
Solute Diffusion-Dominated
Source type that has been used to simulate the release of contaminants from stabilized (e.g., grouted tank or tank ancillary) wastes. With little or no advection through the waste container, the release can be modeled as a diffusion-limited process. Three values, the total solute inventory, the diffusion coefficient within the waste source (m2/s) and the source thickness (m) are required inputs (Zhang et al. 2005). Solute inventory (mass) should be specified in the assumed units for solute (e.g., Ci, pCi, gm, kg, mol, kmol).
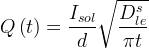
Symbols |
|
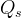 |
source release rate, 1/s |
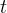 |
time, s |
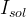 |
solute inventory |
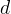 |
vertical depth of waste, m |
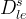 |
effective diffusion coefficient, m2/s |
Solute Variable-Diffusion Dominated
Source type that has been used to simulate the release of contaminants from stabilized (e.g., grouted tank or tank ancillary) wastes. The variable-diffusion dominated model is a variant of the Diffusion-Dominated release model so that the release considers a reduction in diffusion due to the constricted flow path caused by small pores and pore throats within the waste form as shown below. Four values, the total solute inventory, the diffusion coefficient within the waste source (m2/s), the source thickness (m) and the constrictivity factor are required inputs.
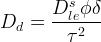
Symbols |
|
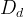 |
variable diffusion coefficient, m2/s |
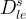 |
effective diffusion coefficient, m2/s |
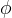 |
diffusive porosity |
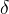 |
constrictivity |
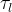 |
aqueous phase tortuosity |
![]() Species Source Options
Species Source Options
![]() Species Source Options
Species Source Options
Species
Source type where the species are injected/withdrawn into/from the node(s) at the specified rate during the indicated time period. The rate specified in the Source Card is for a single node. Therefore, if a source is applied over several nodes, the total species rate of injection/withdrawal should be divided between these nodes.
References
Zhang, ZF, VL Freedman, SR Waichler, and MD White. 2004. 2004 Initial Assessments of Closure for the S-SX Tank Farm: Numerical Simulations, PNNL-14604, Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, Richland, WA.
Zhang, ZF, VL Freedman, SR Waichler, and SK Wurstner. 2005. 2005 Closure Assessments for S-SX Tank Farms: Numerical Simulations, PNNL-15399, Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, Richland, WA.
STOMP User Guide Home
- Simulation Title Card
- Solution Control Card
- Grid Card
- Inactive Nodes Card
- Rock Soil Zonation Card
- Mechanical Properties Card
- Hydraulic Properties Card
- Saturation Function Card
- Aqueous Relative Permeability Card
- Directional Aqueous Relative Permeability Cards
- Solute/Fluid Interaction Card
- Solute/Porous Media Interaction Card
- Initial Conditions Card
- Boundary Conditions Card
- Source Card
- Output Control Card
- Surface Flux Card
