Water Mass Conservation Equation
The water mass conservation equation equates the time rate of change of water mass within a control volume with the flux of water mass crossing the control volume surface.
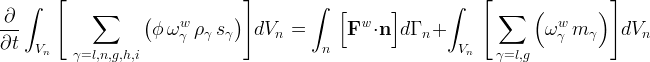
where, water (w) can exist in the aqueous (l), nonaqueous liquid (n), gas (g), hydrate (h) and ice (i) phases under equilibrium conditions, depending on the operational mode.
Water flux is a combination of advective and diffusive components:
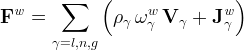
where V is the Darcy velocity.
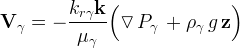
Diffusive fluxes of water through the mobile phases are computed from gradients in molar concentration, considering molecular diffusion, but ignoring hydraulic dispersion;
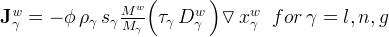
where a combined diffusion-dispersion coefficient, D, replaces the classical Fickian diffusion coefficient.
In STOMP-W, -WAE, -WS, -WASE, and -WAS, there is an osmotic flux term, which accounts for the flow of aqueous fluid by osmotic pressure for simulations with coupled salt transport.
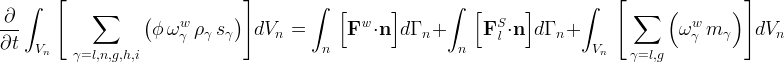
where
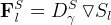
![]() Dissolution of water in the NAPL phase is neglected in all operational modes except STOMP-HYDT-KE.
Dissolution of water in the NAPL phase is neglected in all operational modes except STOMP-HYDT-KE.
![]() Phase partitioning of water mass is computed assuming equilibrium conditions, implying that in geologic media the time scale for thermodynamic equilibrium is significantly shorter for component transport.
Phase partitioning of water mass is computed assuming equilibrium conditions, implying that in geologic media the time scale for thermodynamic equilibrium is significantly shorter for component transport.
![]() Following the low solubility assumption for dissolved air and oil in the aqueous phase, water diffusion-dispersion through the aqueous phase is neglected.
Following the low solubility assumption for dissolved air and oil in the aqueous phase, water diffusion-dispersion through the aqueous phase is neglected.
Symbols |
|
| Vn | volume of element n, m3 |
| l | aqueous liquid phase |
| n | nonaqueous liquid phase |
g |
gaseous phase |
| h | hydrate phase |
| i | ice |
| φ | porosity |
| ργ | density of phase γ, kg/m3 |
| sγ | saturation of phase γ |
| ωγW | mass fraction of water in phase γ |
| Γn | surface of element n, m2 |
| FW | Flux of water, kg/m2s |
| n | unit surface normal vector |
| Vγ | Darcy velocity vector of phase γ, m/s |
| DγW | Diffusive-dispersive flux of water for phase γ, kg/m2s |
| krγ | relative permeability of phase γ |
| k | intrinsic permeability |
| μγ | kinematic viscosity of phase γ, Pa s |
| Pγ | pressure of phase γ, Pa |
| g | acceleration of gravity, m/s2 |
| z | unit gravitational direction vector |
| MW | molecular weight of water, kg/kg mol |
| Mγ | molecular weight of phase γ, kg/kg mol |
| τγ | phase tortuosity for phase γ |
| xγW | mole fraction of water in phase γ |
